What is stroke?
A stroke is a sudden brain attack which is caused by an interruption of blood flow to the brain usually because of a blockade or a burst blood vessel. Brain cells need a constant supply of oxygen from the blood. Without an adequate blood supply, brain cells become damaged. As a result of this damage, a person who has had a stroke may have difficulty with movement often on one side of the body, difficulty communicating and poor coordination and balance.
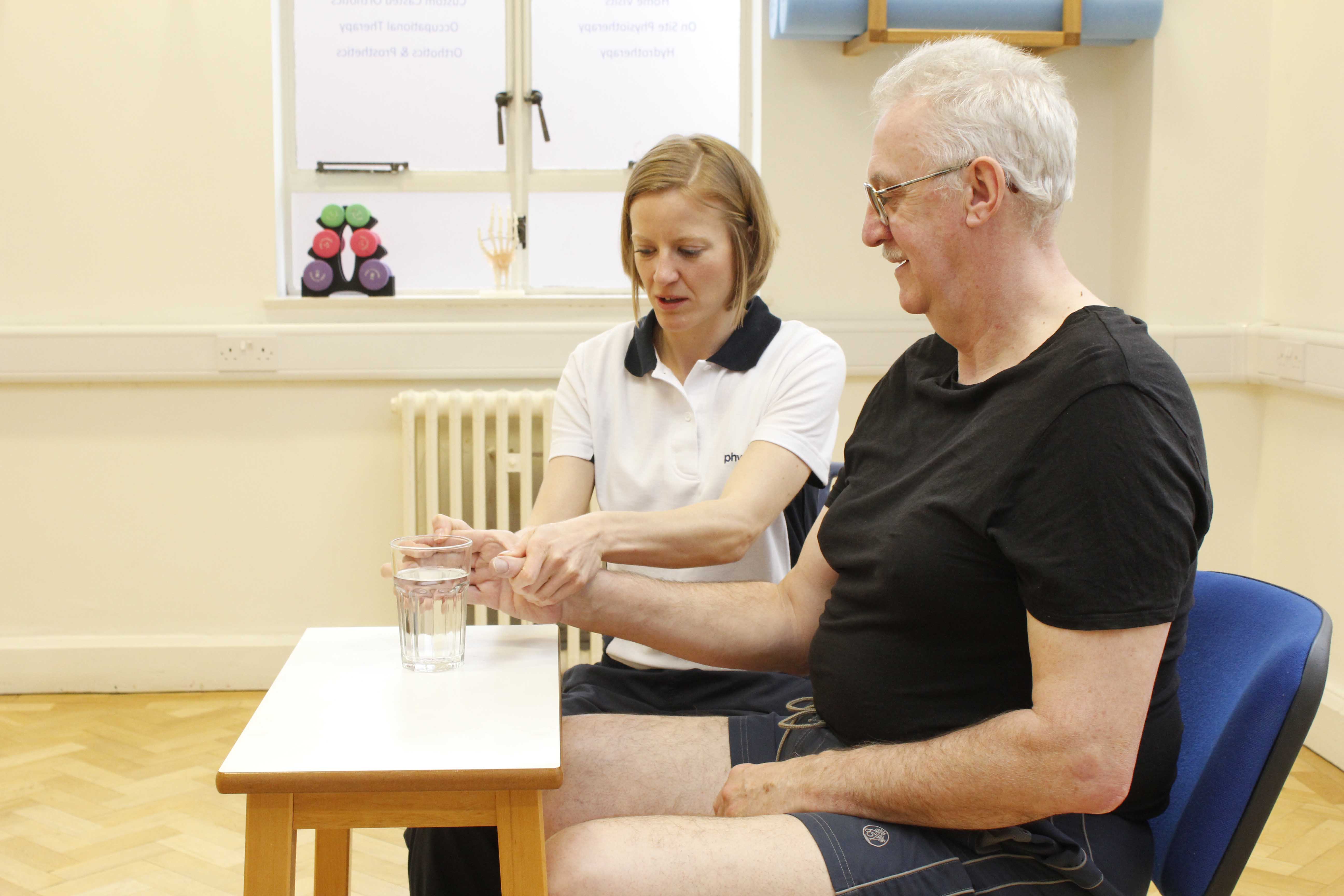 Above: Fine motor skill exercises to rehabilitate greater independance following stroke
Above: Fine motor skill exercises to rehabilitate greater independance following strokeDiagnosis of stroke
A stroke is a medical emergency. It is important to act fast if a person is suspected of having a stroke in order to try and save threatened brain tissue and minimising the damage. The symptoms of a stroke depend on the area of the brain which has been affected.
The symptoms are usually distinct because they happen quickly causing:
- Numbness or weakness of the face, arm, or leg (especially on one side of the body)
- Confusion, trouble speaking or understanding speech
- Trouble seeing in one or both eyes
- Problems walking, dizziness, loss of balance or coordination
- Severe headache with no known cause
The Face Arm Speech Test (FAST) can be used to help anyone diagnose the symptoms of a stroke quickly.
What causes stroke?
There are two main causes of stroke that be classified as either hemorrhagic or ischemic.
- Ischaemic stroke is a lack of blood supply to the brain caused by a blood clot. It is the most common form of stroke. For example, an atheroma is a fatty lump which can develop in the arteries, blocking the artery and interrupting blood flow to the brain.
- Hemorrhagic stroke is bleeding in the brain caused by a weakened blood vessel in the brain that bursts. This can happen in different areas of the brain.
What are the effects / symptoms of stroke?
The effects a stroke depend on the area of the brain it affects. The most common long term effects include:
- Weakness or paralysis on one side of the body with partial or complete loss of voluntary movement.
- Difficulty with walking, movement or coordination
- Poor balance
- Loss of sensation in on one side of the body
- Difficulties with speech and language
- Weak face muscles
- Swallowing difficulties, which can cause trouble with eating or drinking.
- Cognitive difficulties, such as thinking, attention and memory.
- Behaviour and mood changes.
- Difficulties with bowel or bladder control (incontinence).
- Fatigue
- Loss of independence
Physiotherapy for stroke
People who have suffered from a stroke benefit from specialist neurological physiotherapy. Our dedicated neurological physiotherapists at Physio.co.uk understand the difficulties a person will face following a stroke. For the best possible recovery, it is important to start physiotherapy as soon as possible. Physiotherapy treatment will advise and support you throughout your treatment and maximise your potential in order that long term improvements can be achieved.
Physio.co.uk commonly see individuals who have been discharged from the NHS following a stroke with “no rehab potential” that go on to make significant improvements. This can often be many years following their stroke.
The neurological physiotherapists at Physio.co.uk will set short and long term goals tailored to your needs to help promote independence and improve your quality of life. Physiotherapy treatment will be focused around:
- Increasing control of movement of the arms, legs and trunk
- Preventing muscle shortening
- Advise on positioning
- Promoting normal movement
- Encouraging movement of affected limb
- Increasing ability to roll/move in bed/sit/stand
- Promoting activities of daily living
- Increasing muscle strength
- Improving balance and posture
- Improving safety
- Increasing energy levels
- Reducing pain and muscle spasms
- Promoting independence
- Improving quality of life
During treatment sessions our specialised physiotherapists will lead you through a graduated programme of functional exercises which include:
- Muscle strength training to reduce muscle weakness.
- Muscle stretching to help lengthen tight muscles and reduce stiffness.
- Exercises to build stamina and reduce fatigue.
- Repetitive exercise to recruit muscles and improve function.
- Exercises to get the affected side of the body working more effectively.
- Correcting and varying position to improve balance and coordination.
- Teaching transfers (getting in and out of a wheelchair, bed, car, shower/bath and onto and off a toilet).
- Orthotic devices and walking aids to encourage the foot to lift upwards when stepping and prevent injury.
- Hydrotherapy treatment.
- Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES) to stimulate the nerve supplying the leg and help lift the foot upwards to improve the quality of walking.

 0330 088 7800
0330 088 7800